Introduction: What is Maldivian Cuisine?
Maldives is an island nation located in the Indian Ocean and is known for its beautiful beaches and clear blue waters. It is also famous for its cuisine, which is a blend of Indian, Sri Lankan, Arabic and East African influences. Maldivian cuisine is mainly based on seafood, coconut, and starches like rice and cassava. The use of spices and seasonings is also prominent in Maldivian cuisine, giving it a unique distinct flavor.
The Impact of Geography on Maldivian Cuisine
The geography of Maldives has played a significant role in shaping its cuisine. Being surrounded by water on all sides, seafood is the heart of Maldivian cuisine. Fish such as tuna, barracuda, and mahi-mahi are commonly used in Maldivian dishes. Coconut, which is another essential ingredient, is found in abundance on the islands. The cuisine also features a variety of tropical fruits and vegetables, including papayas, pineapples, yams, and sweet potatoes.
Staple Foods in Maldivian Cuisine
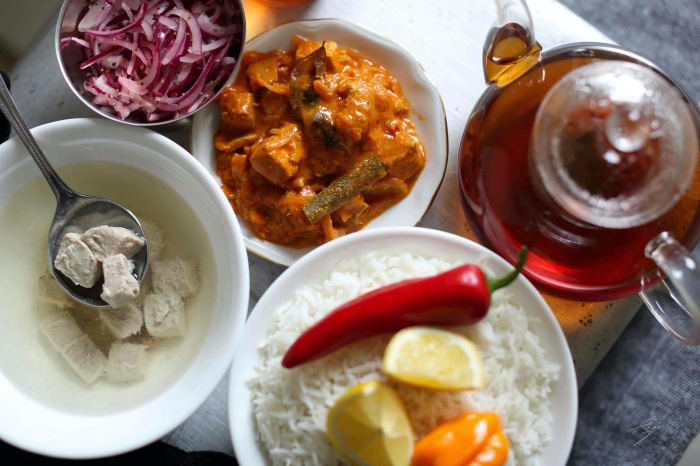
Rice is a staple food in Maldives and is usually served with fish, curries, or vegetables. Another popular starch is cassava, which is a root vegetable found in abundance in Maldives. It is usually boiled or fried and served as a side dish or a snack. Mas huni, a popular breakfast dish, is made from shredded smoked tuna, grated coconut, and onions, and is served with roshi (a flatbread) or chapati.
Spices and Seasonings in Maldivian Cuisine
The cuisine of Maldives is known for its bold and flavorful spices. Cumin, coriander, cardamom, cinnamon, and turmeric are commonly used in Maldivian dishes. Chili is also a staple in the cuisine, and most dishes are spicy. Curry leaves, lemongrass, and pandan leaves are also used to add flavor to dishes.
Seafood: The Heart of Maldivian Cuisine
As mentioned earlier, seafood is the heart of Maldivian cuisine. Tuna is the most commonly used fish in Maldivian dishes, and it is usually served grilled, fried, or curried. Rihaakuru, a thick paste made from tuna, is also a popular ingredient in many dishes. Fish curry, garudhiya (a fish broth), and mas riha (a tuna curry) are some of the most popular seafood dishes in Maldives.
Desserts and Beverages in Maldivian Cuisine
Maldives is famous for its sweet treats, which are usually made from coconut and jaggery (a type of sugar). Foni boakibaa, a coconut cake, and bondi, a sweetened coconut milk pudding, are popular desserts in Maldives. Tea is the most commonly consumed beverage in Maldives, and it is usually served with sugar and milk. The traditional Maldivian drink, Raa, is a type of palm wine made from the sap of the coconut palm. It is a popular alcoholic beverage in Maldives, especially among the older generations.
In conclusion, Maldivian cuisine is a unique blend of flavors and ingredients that reflect the diverse influences of the region. Its emphasis on seafood, coconut, and spices, along with its use of locally grown produce, makes it a cuisine worth exploring and experiencing.