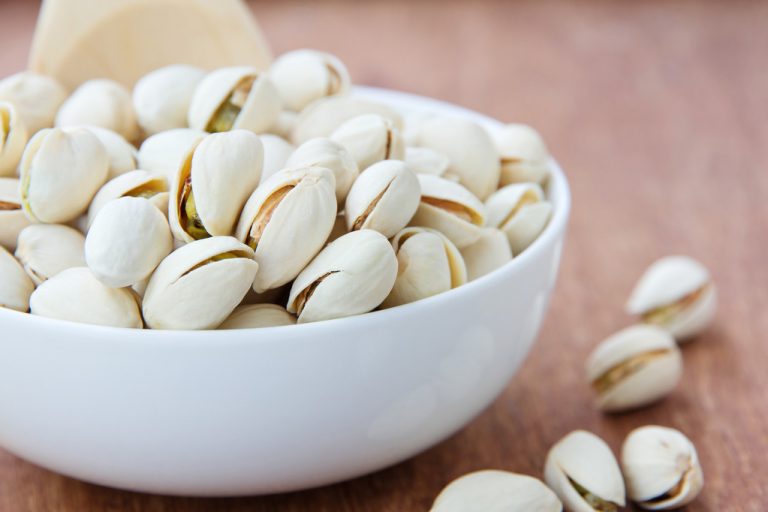
Pistachios are a healthy and tasty snack between meals. The delicious nuts contain many healthy ingredients. We’ll show you which ones.
Pistachios are healthy: the ingredients
Pistachios are delicious and have a long list of healthy nutrients. This includes:
Potassium (with 1005 mg vs. 393 mg almost three times as much as bananas!)
phosphorus
beta-carotene
Vitamin B6
thiamine
magnesium
These and other ingredients contribute to the fact that pistachios are very healthy:
Because pistachios have high bioavailability, the nutrients in the nuts are very easily absorbed in your stomach.
Pistachios have a lot of antioxidants and are therefore particularly anti-inflammatory. The nuts increase the level of the important antioxidant lutein in the human body, which is why they are also extremely good for your eye health.
The polyphenols and tocopherols in the small green seeds are even said to prevent cancer and heart disease.
If you want to lose weight, pistachios are an ideal snack for you: they have a lot of unsaturated fatty acids, amino acids and proteins, which has been proven to fill you up faster and help with weight loss. In one study, they significantly helped some overweight subjects with their diet.
But keep in mind that pistachios are very nutritious: 100 grams contain over 600 kilocalories. Therefore, you should not overdo it with them and rather consume them in smaller amounts if you want to lose weight.
Pistachios help with diabetes: they reduce triglycerides in the body, which are usually very high in diabetic patients. Intestinal bacteria, which are directly associated with type 2 diabetes, are said to be regulated by pistachios. Another study was even able to demonstrate a positive effect on blood sugar levels.
In general, pistachios have a good influence on your intestinal microbes. The short-chain fatty acid butyrate produced by the bacteria can not only prevent indigestion, but also prevent colon cancer.
Pistachios are high in healthy fats. The unsaturated fatty acids in nuts not only help you lose weight, they are also good for your heart and cholesterol levels. They have been shown to lower the unhealthy LDL cholesterol in your blood. Even young men who were already following a healthy Mediterranean diet were particularly good at pistachios: they also noticeably lowered their cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Pistachios and their risks
Although pistachios do not have any particularly harmful ingredients, they can become downright toxic if stored incorrectly: the investigative Swiss television program for consumer protection “Kassensturz” tested pistachios together with the sister station “À Bon Entendeur”. They discovered a high level of aflatoxins in half of the 14 different pistachio packs.
If pistachios are not stored dry, they can be attacked by mold. These convert into the dangerous, hepatoxic mold toxin aflatoxin. It can severely damage the liver and even lead to lung cancer.
Since pistachios are only dried slowly in the sun in Iran, for example, the risk of mold is high. The gentle process preserves the nutrients better and intensifies the taste, but unfortunately the moisture also makes the nuts more susceptible to mold. Of course, this can also happen in industrial production as soon as they are not stored dry enough.
In addition, the consumer protection magazines report that pesticides were also found in the tested products. For the most part, however, they are below the legal limit values – with the exception of two products: one Ültje product exceeded the legal values by a full 200%. However, Ültje blames this infestation on uneven distribution in the load. High levels of both aflatoxins and pesticides were also found in a Geneva market product.
Even if the products from the market often help small farmers or importers, they often mean less control than with large food manufacturers.

Background information on healthy pistachios
We know the pistachio as a tasty, green nut with a hard shell and a crunchy core. However, this nut is the stone fruit of the pistachio tree. More than 10,000 years ago, pistachios were cultivated in the Middle East, especially in Syria. There they are still a delicacy today, part of the long cultural history of many countries throughout the area:
For a long time, the pistachio was considered an exclusively royal delicacy that was withheld from the “common people”. But over time, it spread among travelers, merchants, and common folk. Because of its long shelf life and high nutritional value, it was popular with everyone. Over the years they conquered the entire world and came to us during the Middle Ages. The largest cultivation areas are found today in Iran, the USA, Turkey and China.
With us, the pistachios are mostly roasted and salted and eaten directly as a snack. In the Middle East, Asia and the Balkans, it is processed into a wide variety of delicious sweets: halva, baklava, maamoul or kunafah. These sinful pastries are usually created and processed with lots of sugar, honey, syrup and rose water. The pistachio serves both as a basic ingredient and for refinement. You can find many of these in oriental grocery stores.
But pistachios are also processed into various sweet specialties in Italy: the addition of pistachios gives the Sicilian almond pastry Pasta di Mandola an incredibly intense taste. Amaretti, cantuccini and cannoli are also often refined with pistachios.