Introduction: Dominican Cuisine
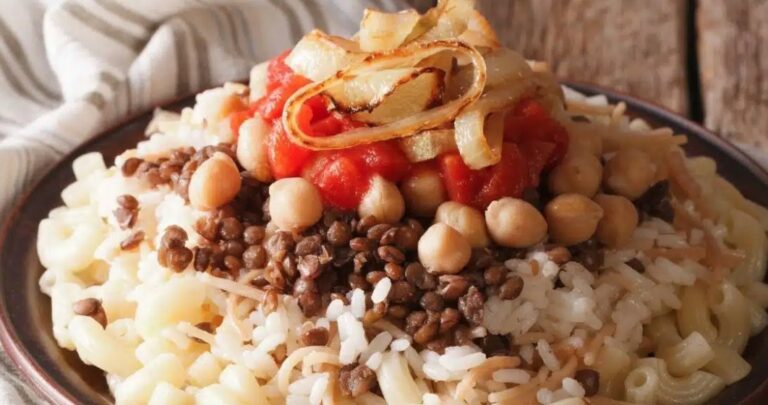
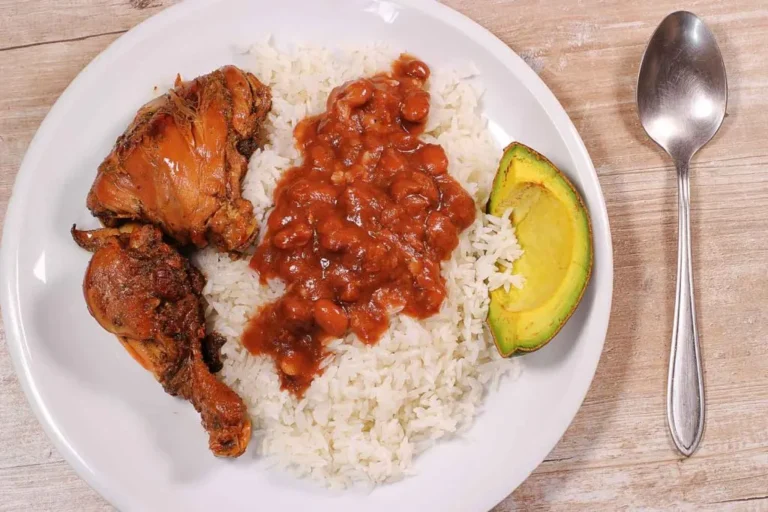
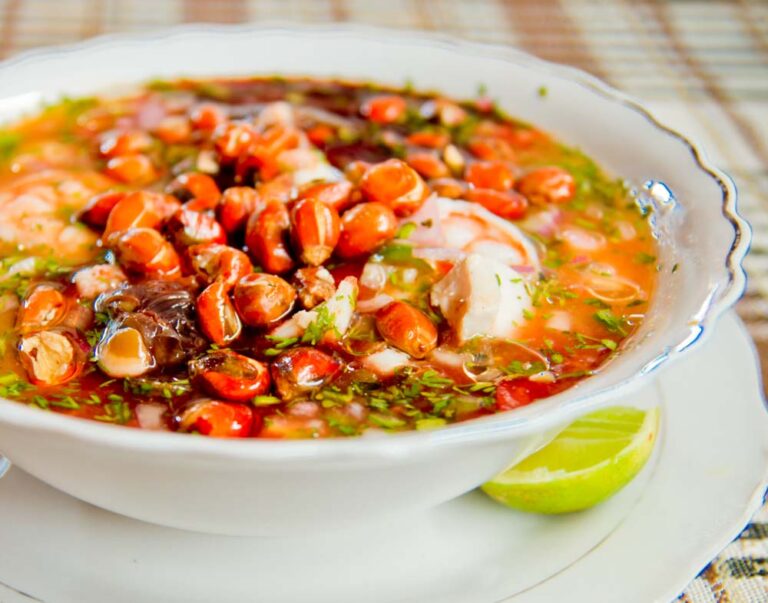
Dominican cuisine is a vibrant and flavorful fusion of African, European, and indigenous Taino influences. The country’s fertile soil and tropical climate have also contributed to a rich culinary tradition that boasts a wide variety of fresh fruits, vegetables, and spices. Dominican dishes are known for their bold and complex flavors, which are often enhanced by the use of sauces and condiments.
Essential ingredients in Dominican cooking
Dominican cooking relies heavily on staples like rice, beans, plantains, and yucca, which are often paired with meat or seafood. The cuisine also features a variety of fresh herbs and spices, including cilantro, garlic, onions, oregano, and cumin. Coconut milk and various citrus fruits are frequently used to add depth and complexity to dishes. The use of sauces and condiments is an integral part of Dominican cooking, as they can elevate the flavors of any dish.
Sauces and condiments in Dominican cuisine
Dominican cuisine features a range of sauces and condiments that can be used to add flavor, heat, and acidity to dishes. Sofrito, chimichurri, mojo, and aji are some of the most popular condiments in the Dominican Republic.
Sofrito: The heart of Dominican cooking
Sofrito is a versatile sauce that is used as a base for many Dominican dishes. It is made by blending onions, garlic, peppers, cilantro, and other herbs and spices together. Sofrito adds a depth of flavor and richness to stews, soups, and rice dishes.
Chimichurri: A popular sauce in Dominican dishes
Chimichurri is a tangy and flavorful green sauce that is often served alongside grilled meats. It is made with parsley, garlic, red pepper flakes, vinegar, and oil. Chimichurri can also be used as a marinade or dressing for salads.
Mojo: A citrusy sauce with a kick
Mojo is a zesty sauce that is made with sour oranges, garlic, and oil. It is often served alongside roasted pork or chicken. Mojo adds a bright and tangy flavor to dishes and can also be used as a marinade.
Aji: A hot sauce with a Caribbean twist
Aji is a spicy condiment that is made with hot peppers, vinegar, garlic, and other spices. It is a staple in many Caribbean countries and is often used to add heat to dishes like meats, rice, and beans. Aji can also be used as a dip or spread.
Summary: Explore the flavors of Dominican cuisine
Sauces and condiments are an essential part of Dominican cuisine, adding depth, richness, and zest to traditional dishes. Sofrito, chimichurri, mojo, and aji are just a few of the sauces that are commonly used in Dominican cooking. Whether you are a fan of spicy or tangy flavors, there is a sauce or condiment to suit every taste in this vibrant and flavorful cuisine.