In the trade, a distinction is made between refined and native oils. But what exactly are refined oils? Here’s a little about their pros and cons.
Manufacturing makes the difference
Refined and native oils differ in their production: Native oils are gently cold-pressed. This means that they are manufactured at low temperatures and without the use of chemicals. Due to the gentle processing, many healthy ingredients are retained, such as vitamins and unsaturated fatty acids.
Refined oils, on the other hand, are extracted under the influence of heat and chemicals.
The oil is hot pressed.
Solvents such as hexane or light petroleum are used during extraction.
This method is used to extract more oil than cold pressing. However, refined oils are not unhealthy or toxic because of this: the chemical residues are then removed from the oil. The oil is heated up to 240°C for several hours for cleaning. This process is called refining.
This means that there are no longer any unwanted chemical substances in the oil. However, the oil also loses vitamins, unsaturated fatty acids and taste. This means that the oil is not unhealthy or harmful, but it is also not as healthy as native oils. However, refined oils also have advantages in their use.
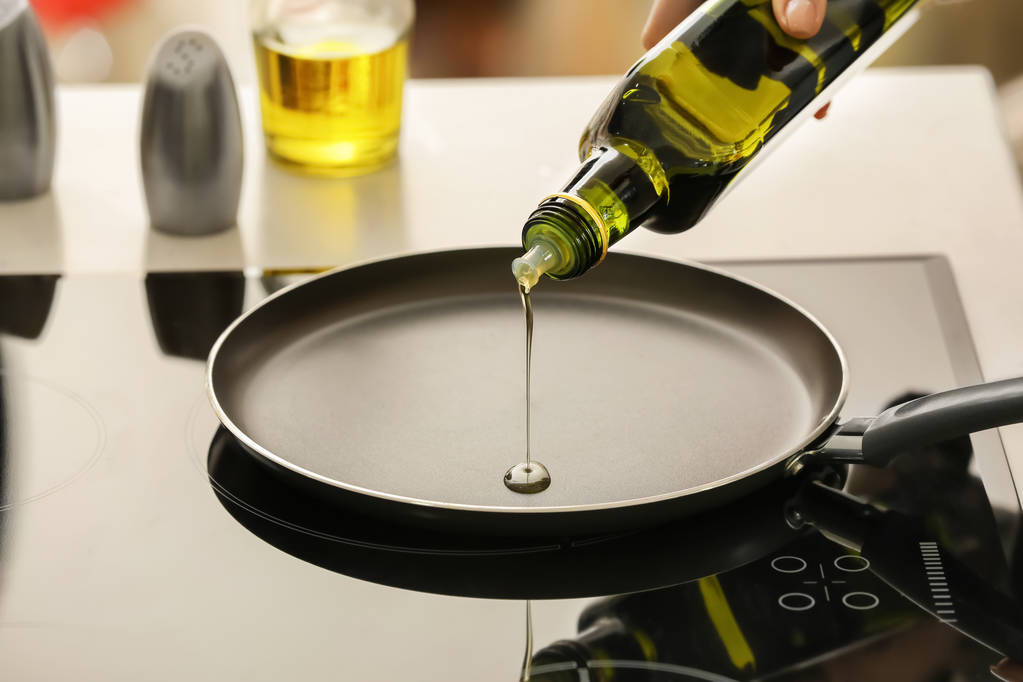

Pros and cons of refined oil
Advantages are:
Refined oil is more heat resistant. Only use refined oils for hot frying. They are also better suited for cooking. When native oils are heated too much, smoke and pollutants are formed. So for this purpose, refined oils are healthier than virgin oils.
Refined oils are cheaper to produce than virgin oils. Accordingly, they also cost less in the store.
The more heavily treated oils tend to be more tasteless. This can be an advantage for cooking if you don’t want the oil to taste too bad.
Due to the strong treatment, refined oils have a longer shelf life than native oils.
Disadvantages are:
The hot pressing and long heating takes more energy.
Refined oil contains fewer valuable ingredients than virgin oil, such as vitamins and unsaturated fatty acids.
The fact that refined oils are less flavorful can also be a disadvantage. In salads, the taste of native oil is quite appropriate.
Harmful trans-fatty acids can be produced during deodorization, a sub-process of refining.
In general, refined oils are not inherently unhealthy. For some purposes such as cooking and frying, they are very well suited because of their heat resistance. Depending on the purpose for which you want to use the oil, you should choose the right oil.