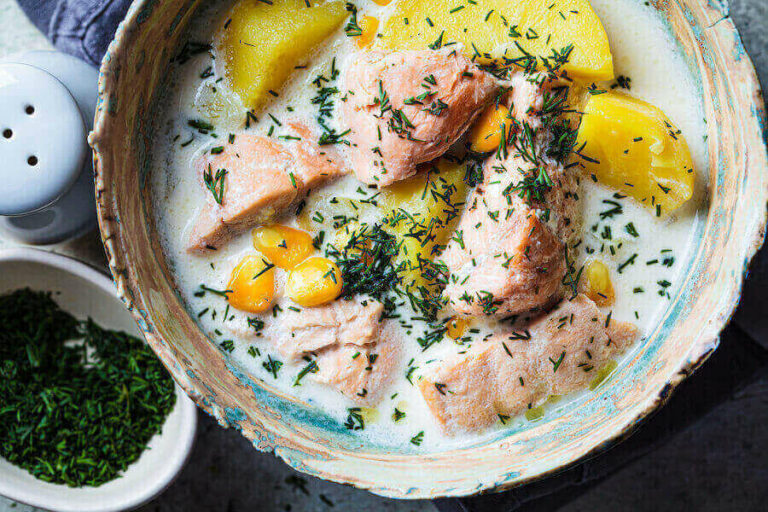Introduction: Montenegrin cuisine
Montenegro is a small country located on the Adriatic coast in Southeast Europe. Its cuisine is a blend of traditional Balkan and Mediterranean flavors, with influences from neighboring countries such as Italy and Greece. Montenegrin cuisine is known for its hearty dishes, rich flavors, and fresh ingredients.
Coastal location and its impact
Montenegro’s coastal location has had a significant impact on its cuisine. The country’s long coastline provides abundant access to fresh seafood and fish, which are staples in Montenegrin cuisine. In addition to seafood, the coastal region is also rich in olive groves, vineyards, and herb gardens, which have helped shape the country’s culinary traditions.
Fresh seafood and fish dishes
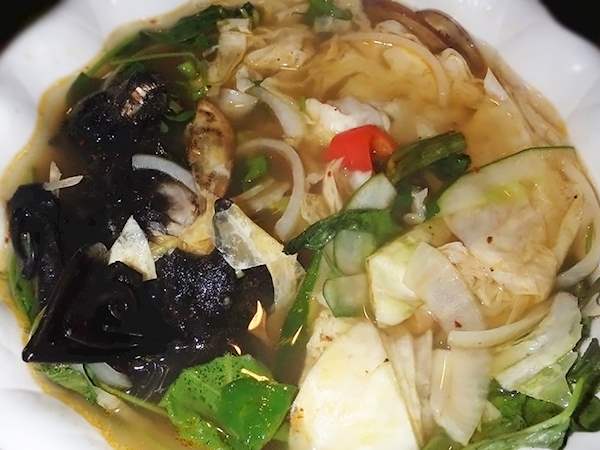
Seafood and fish are essential ingredients in Montenegrin cuisine. Some of the popular seafood dishes include black risotto, grilled squid, and stuffed calamari. Other seafood specialties include octopus salad, sea bass, and mussels. Montenegrins also enjoy freshwater fish, such as trout and carp, which are prepared in various ways, including grilled, baked, or fried.
Mediterranean spices and herbs
Montenegrin cuisine is characterized by the use of Mediterranean spices and herbs, such as rosemary, thyme, oregano, and sage. These herbs are used to flavor fish and meat dishes, as well as sauces and salads. Montenegrin cuisine also features garlic, onions, and peppers, which add depth and flavor to many dishes.
Olive oil, wine and cheese culture
Olive oil is a staple in Montenegrin cuisine, as the country has a long tradition of olive oil production. The oil is used for cooking, as a dressing for salads, and as a dip for bread. Montenegro is also known for its wine culture, with some of the best wines produced in the coastal region. Cheese is also an important ingredient in Montenegrin cuisine, with varieties such as kolasin, pljevlja, and niksicki being the most popular.
Fusion of cultures and modern influences
Montenegrin cuisine has been shaped by various cultural influences over the years. The country’s proximity to Italy has led to the incorporation of Italian dishes such as pasta and pizza into Montenegrin cuisine. Turkish and Balkan influences have also contributed to the country’s culinary traditions. In recent years, modern influences have also been introduced, with fusion cuisine becoming increasingly popular in Montenegro’s larger cities.
In conclusion, Montenegrin cuisine is a unique blend of Balkan and Mediterranean flavors, shaped by the country’s coastal location and historical influences. Fresh seafood, Mediterranean spices and herbs, olive oil, wine, and cheese are some of the essential ingredients that make up Montenegrin cuisine. As the country continues to evolve, its culinary traditions will no doubt continue to be influenced by new trends and cultural influences.