Eating right is just as important to building muscle as exercise: it depends on what you eat and when. You can read here what else you should pay attention to when it comes to your diet.

Muscle building through diet: Eating healthy is important
Muscles grow when you challenge them in training. However, it is also important to eat a diet that provides the body with sufficient energy and the necessary material. Otherwise he cannot build new muscles.
To build muscle through nutrition, you need the following nutrients in particular:
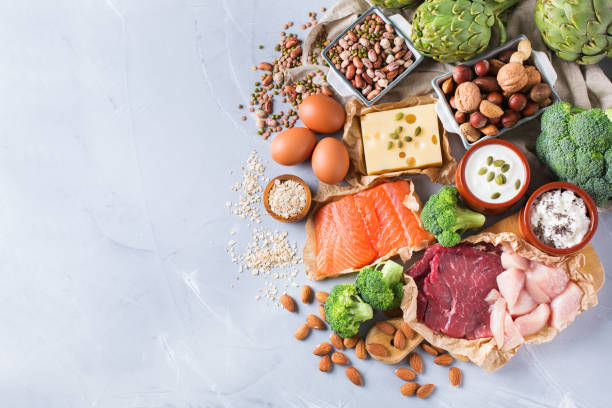
Proteins: The amino acids in the proteins are the building blocks of the muscle cells.
The minerals zinc and magnesium: They support the development of muscles.
In order for your body to be able to complete the training workload, it needs energy and all the essential vitamins and minerals:
Carbohydrates: They provide the energy for driving the body.
Minerals and water: Do you sweat out when you are physically active? Your water and mineral balance should always be balanced.
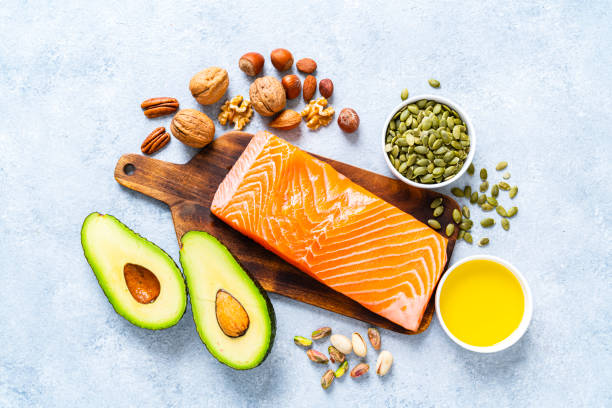
Vitamins and fats: They round off a healthy diet and ensure that you feel good in your body.
Scientists advise amateur athletes to eat a balanced and varied diet: it should be rich in carbohydrates but low in fat. Whenever possible, use food from organic farming and from your region. They are not only healthier and free of pesticides – you also contribute to climate protection by supporting short transport routes.
A healthy diet supports muscle building: It creates resilient muscles that can fulfill their natural tasks. Well-trained muscles are not only a visual stimulus, but also important for your health, for example for the trunk muscles. By building muscle, you prevent back pain and reduce postural damage to the shoulders and neck. These complaints are widespread today: Anyone who has to sit for a long time, for example at a desk in front of the computer, neglects their core muscles and needs a balance.
Building muscle with a high-protein diet
Proteins contain essential amino acids that you need to build muscle. However, the following formula does not apply here: A lot of material also helps a lot. The Apotheken-Umschau explains that a protein-rich diet only helps to build muscle if you train at the same time. During training, the body has an increased need for proteins and also uses them to build muscles. Without training, he excretes the excess proteins unused.
According to a study, the protein requirement for active athletes is between 1.2 and 1.4 grams per kilogram of body weight. With intensive weight training, the value can rise to 1.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. In comparison: the average daily protein requirement is around 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight.
Do you need animal protein to build muscle?
According to nutritionists, it is not the pure mass of the proteins that is decisive for building muscle, but their biological value. The biological value states how high the proportion of proteins from food is that the human body can actually utilize.
In this respect, the proteins of livestock are ahead – but meat and sausage often contain saturated fatty acids that put a strain on the body. Experts therefore generally recommend a mixed diet of vegetable proteins and animal foods that contain little fat. These include dairy products, lean meat or eggs.
At PETA, vegan nutritionists have their say. For them, plant-based protein sources have an advantage because they provide a nutrient combination of carbohydrates and fiber. For example, legumes such as beans, lentils and peas contain all the important nutrients for muscle building. This makes them a power food for athletes.
Other plant-based protein sources include:
Soybeans, including tofu, soy drinks or seitan and tempeh
Nuts such as Brazil nuts, peanuts, almonds or cashew nuts
Whole grains and pseudo-cereals like hemp and amaranth

Minerals also play a role in building muscle through nutrition
In order for the body to be able to process the amino acids from the proteins, it needs zinc and magnesium.
Zinc: Is directly involved in building muscle cells.
According to the medical portal Onmeda, the recommended requirement for men is 11 to 17 milligrams per day. For women it is slightly lower, at 7 to 10 milligrams per day.
Your body gets new zinc from dark meat (e.g. lean beef), dairy products or eggs.
It’s also vegan: legumes, tofu, nuts and whole grains also contain zinc. Attention: In some cases, the body is less able to absorb zinc from plant sources. Fruit acids and the fermentation or roasting of food help him to do this.
Magnesium: Ensures that the muscles can work optimally. It is also involved in energy metabolism and the body needs it to process protein. Magnesium is therefore indispensable for building muscle through nutrition.
According to Onmeda, the daily requirement for men is about 350 milligrams. Women get by with 300 milligrams.
Magnesium is abundant in plant foods. These include whole grain products, oatmeal, nuts, sunflower seeds, legumes and green vegetables.